Hirschsprung's disease
Definition
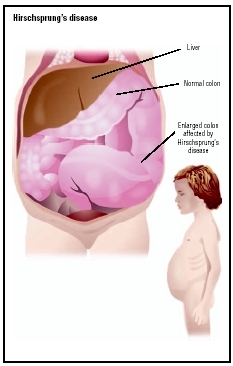
Hirschsprung's disease, also known as congenital megacolon or aganglionic megacolon, is an abnormality in which certain nerve fibers are absent in segments of the bowel, resulting in severe bowel obstruction.
Description
Hirschsprung's disease is caused when certain nerve cells (called parasympathetic ganglion cells) in the wall of the large intestine (colon) do not develop before birth. Without these nerves, the affected segment of the colon lacks the ability to relax and move bowel contents along. This causes a constriction and as a result, the bowel above the constricted area dilates due to stool becoming trapped, producing megacolon (enlargement of the colon). The disease can affect varying lengths of bowel segment, most often involving the region around the rectum. In up to 10 percent of children, however, the entire colon and part of the small intestine are involved.
Demographics
Hirschsprung's disease occurs once in every 5,000 live births, and it is about four times more common in males than females. Between 4 percent and 50 percent of siblings are also afflicted. The wide range for recurrence is due to the fact that the recurrence risk depends on the gender of the affected individual in the family (i.e., if a female is affected, the recurrence risk is higher) and the length of the aganglionic segment of the colon (i.e., the longer the segment that is affected, the higher the recurrence risk).
Causes and symptoms
Hirschsprung's disease occurs early in fetal development when, for unknown reasons, there is either failure of nerve cell development, failure of nerve cell migration, or arrest in nerve cell development in a segment of bowel. The absence of these nerve fibers, which help control the movement of bowel contents, is what results in intestinal obstruction accompanied by other symptoms.
There is a genetic basis to Hirschsprung's disease, and it is believed that it may be caused by different genetic factors in different subsets of families. Proof that genetic factors contribute to Hirschsprung's disease is that it is known to run in families, and it has been seen in association with some chromosome abnormalities. For example, about 10 percent of children with the disease have Down syndrome (the most common chromosome abnormality). Molecular diagnostic techniques have identified many genes that cause susceptibility to Hirschsprung's disease. As of the early 2000s, there are a total of six genes: the RET gene, the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene, the endothelin-B receptor gene, endothelin converting enzyme, the endothelin-3 gene, and the Sry-related transcription factor SOX10. Mutations that inactivate the RET gene are the most frequent, occurring in 50 percent of familial cases (cases which run in families) and 15 to 20 percent of sporadic (non-familial) cases. Mutations in these genes do not cause the disease, but they make the chance of developing it more likely. Mutations in other genes or environmental factors are required to develop the disease, and these other factors are not understood. Also, among children with Hirschsprung's disease, some 2–5 percent have cardiac defects.
For persons with a ganglion growth beyond the sigmoid segment of the colon, the inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant with reduced penetrance (risk closer to 50 percent). For persons with smaller segments involved, the inheritance pattern is multifactorial (caused by an interaction of more than one gene and environmental factors, risk lower than 50 percent) or autosomal recessive (one disease gene inherited from each parent, risk closer to 25 percent) with low penetrance.
The initial symptom is usually severe, continuous constipation . A newborn may fail to pass meconium (the first stool) within 24 hours of birth, may repeatedly vomit yellow or green colored bile, and may have a distended (swollen, uncomfortable) abdomen. Occasionally, infants may have only mild or intermittent constipation, often with diarrhea .
While two-thirds of cases are diagnosed in the first three months of life, Hirschsprung's disease may also be diagnosed later in infancy or childhood. Occasionally, even adults are diagnosed with a variation of the disease. In older infants, symptoms and signs may include anorexia (lack of appetite or inability to eat), lack of the urge to move the bowels or empty the rectum on physical examination, distended abdomen, and a mass in the colon that can be felt by the physician during examination. It should be suspected in older children with abnormal bowel habits, especially a history of constipation dating back to infancy and ribbon-like stools.
Occasionally, the presenting symptom may be a severe intestinal infection called enterocolitis, which is life threatening. The symptoms are usually explosive, watery stools and fever in a very ill-appearing infant. It is important to diagnose the condition before the intestinal obstruction causes an overgrowth of bacteria that evolves into a medical emergency. Enterocolitis can lead to severe diarrhea and massive fluid loss, which can cause death from dehydration unless surgery is done immediately to relieve the obstruction.
Diagnosis
Hirschsprung's disease in the newborn must be distinguished from other causes of intestinal obstruction. The
Treatment
Hirschsprung's disease is treated surgically. The goal is to remove the diseased, nonfunctioning segment of the bowel and restore bowel function. This is often done in two stages. The first stage relieves the intestinal obstruction by performing a colostomy. This procedure creates an opening in the abdomen (stoma) through which bowel contents can be discharged into a waste bag. When the child's weight, age, or condition is deemed appropriate, surgeons close the stoma, remove the diseased portion of bowel, and perform a pull-through procedure, which repairs the colon by connecting functional bowel to the anus. This usually establishes fairly normal bowel function.
KEY TERMS
Anus —The opening at the end of the intestine through which solid waste (stool) passes as it leaves the body.
Barium enema —An x-ray procedure that involves the administration of barium into the intestines by a tube inserted into the rectum. Barium is a chalky substance that enhances the visualization of the gastrointestinal tract on x ray.
Colostomy —A surgical procedure in which an opening is made in the wall of the abdomen to allow a part of the large intestine (the colon) to empty outside the body. Colostomies are usually required because portions of the intestine have been removed or an intestinal obstruction exists.
Enterocolitis —Severe inflammation of the intestines that affects the intestinal lining, muscle, nerves and blood vessels.
Manometry —A technique for measuring changes in pressure.
Meconium —A greenish fecal material that forms the first bowel movement of an infant.
Megacolon —Abnormal dilation of the colon.
Parasympathetic ganglion cell —Type of nerve cell normally found in the wall of the colon.
Prognosis
Overall, prognosis is very good. Most infants with Hirschsprung's disease achieve good bowel control after surgery, but a small percentage of children may have lingering problems with soilage or constipation. These infants are also at higher risk for an overgrowth of bacteria in the intestines, including subsequent episodes of enterocolitis, and should be closely followed by a physician. Mortality from enterocolitis or surgical complications in infancy is 20 percent.
Prevention
Hirschsprung's disease is a congenital abnormality that has no known means of prevention. It is important to diagnose the condition early in order to prevent the development of enterocolitis. Genetic counseling can be offered to a couple with a previous child with the disease or to an affected individual considering pregnancy to discuss recurrence risks and treatment options. Prenatal diagnosis was not available as of 2004.
Parental concerns
Parents should understand that toilet teaching may be delayed in children who have had surgery for Hirschsprung's disease. Children who have had surgical correction of Hirschsprung's disease are also at a higher risk for constipation and dehydration. Increased fluid and fiber intake are usually sufficient to improve these problems.
Resources
BOOKS
McConnell, Elizabeth J., and John H. Pemberton. "Megacolon: congenital and acquired." In Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease , 7th ed. Edited by Mark Feldman et al. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier, 2002.
Wyllie, Robert. "Motility Disorders and Hirschsprung Disease." In Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. Edited by Richard E. Behrman et al. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2004.
PERIODICALS
Halter, J. "Common gastrointestinal problems and emergencies in neonates and children." Clinical Family Practice 6 (September 2004): 731.
Hussain, S. Z. "Motility disorders: Diagnosis and treatment for the pediatric patient." Pediatric Clinics of North America 49 (February 2002): 27–51.
Stewart, D. R. "The genetics of Hirschsprung disease." Gastroenterological Clinics of North America 32 (September 2003): 819–837.
Amy Vance, MS, CGC Rosalyn Carson-DeWitt, MD