Malocclusion
Definition
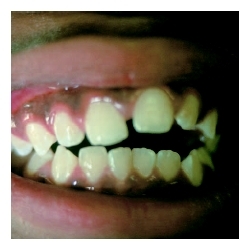
Malocclusion is the misalignment of the upper and lower teeth when biting or chewing.
Description
The word malocclusion literally means "bad bite." The condition may also be referred to as an irregular bite, crossbite, or overbite. Malocclusion may be seen as crooked, crowded, or protruding teeth. It may affect a child's appearance, speech, and/or ability to eat.
Demographics
Most children have some degree of malocclusion. Malocclusion usually does not require treatment except for cosmetic reasons. It is more likely to occur if the parents have malocclusion, the child sucks his or her thumb or a pacifier, or if a tooth is lost prematurely.
Causes and symptoms
Malocclusions are most often inherited, but may be acquired. Inherited conditions include too many or too few teeth, too much or too little space between teeth, irregular mouth and jaw size and shape, and atypical formations of the jaws and face, such as a cleft palate . Malocclusions may be acquired from habits like finger or thumb sucking , tongue thrusting, premature loss of teeth from an accident or dental disease, and possibly from medical conditions such as enlarged tonsils and adenoids that lead to mouth breathing.
Malocclusions may cause no symptoms, or they may produce pain from the increased stress on oral structures. Teeth may show abnormal signs of wear on the chewing surfaces or decay in areas of tight overlap. Chewing may be difficult.
When to call the doctor
A dentist or orthodontist should be consulted if a child's teeth seem to be particularly misaligned or if a child complains of dental or jaw pain.
Diagnosis
Malocclusion is most often found during a routine dental examination. A dentist will check a patient's occlusion by watching how the teeth make contact when the child bites down normally. The dentist may ask the
Treatment
Malocclusion may be remedied by orthodontic treatment. Orthodontics is a specialty of dentistry that manages the growth and correction of dental and facial structures. Braces are the most commonly used orthodontic appliances in the treatment of malocclusion. At any given time, approximately four million people in the United States are wearing braces, most of whom are children and teenagers.
Braces apply constant gentle force to slowly change the position of the teeth, straightening and properly aligning them with the opposing teeth. Braces consist of brackets cemented to the surface of each tooth and wires of stainless steel or nickel titanium alloy. When the wires are threaded through the brackets, they exert pressure against the teeth, causing them to gradually move.
Braces are not removable for daily tooth brushing. To prevent tooth decay , the child must be especially diligent about keeping the mouth clean and removing food particles that become easily trapped. Crunchy foods should be avoided to minimize the risk of breaking the appliance. Hard fruits, vegetables, and breads must be cut into bite-sized pieces before eating. Foods that are sticky, including chewing gum, should be avoided because they may pull off the brackets or weaken the cement. Carbonated beverages may also weaken the cement, as well as contribute to tooth decay. Teeth should be brushed immediately after eating. Special floss threaders are available to make flossing easier.
If overcrowding is creating malocclusion, one or more teeth may be extracted (surgically removed), giving the others room to move. If a tooth has not yet erupted or is prematurely lost, the orthodontist may insert an appliance, called a space maintainer, to keep the other teeth from moving out of their natural position. In severe cases of malocclusion, surgery may be necessary and the patient is referred to another specialist, an oral or maxillofacial surgeon.
Once the teeth have been moved into their new position, the braces are removed, and a retainer is worn until the teeth stabilize in that position. Retainers do not move teeth, they only hold them in place. Often a retainer is initially worn all the time; its use is gradually tapered until it is only worn at night, and eventually not at all.
KEY TERMS
Braces —An orthodontic appliance consisting of brackets cemented to the surface of each tooth and wires of stainless steel or nickel titanium alloy. Braces are used to treat malocclusion by changing the position of the teeth.
Impression —In dentistry, an imprint of the upper or lower teeth made in a pliable material that sets. When this material has hardened, it may be filled with plaster, plastic, or artificial stone to make an exact model of the teeth.
Occlusion —The way upper and lower teeth fit together during biting and chewing. Also refers to the blockage of some area or channel of the body.
Retainer —An orthodontic appliance that is worn to stabilize teeth in a new position.
Space maintainer —An orthodontic appliance that is worn to prevent adjacent teeth from moving into the space left by an unerupted or prematurely lost tooth.
Orthodontic treatment is the only effective treatment for malocclusion not requiring surgery. However, depending on the cause and severity of the condition, an orthodontist may be able to suggest other appliances as alternatives to braces. If the malocclusion is thought to be caused by the child sucking on fingers or a pacifier and the child is stopped early enough, the malocclusion may resolve spontaneously without treatment.
Alternative treatment
There are some techniques of craniosacral therapy that can alter structure. This therapy may allow correction of some cases of malocclusion. If surgery is required, pre- and post-surgical care with homeopathic remedies, as well as vitamin and mineral supplements, can enhance recovery. Night guards are sometimes recommended to ease the strain on the jaw and to limit teeth grinding.
Prognosis
Depending on the cause and severity of the malocclusion and the appliance used in treatment, a patient may expect correction of the condition to take two or more years. Patients typically wear braces 18–24 months, and a retainer for another year. Treatment is faster and more successful in children and teens whose teeth and bones are still developing. The time needed for treatment is also affected by how well the patient follows orthodontic instructions.
Prevention
In general, malocclusion is not preventable. It may be minimized by controlling habits such as thumb sucking. An initial consultation with an orthodontist before a child is seven years of age may lead to appropriate management of the growth and development of the child's dental and facial structures, circumventing many of the factors contributing to malocclusion.
Parental concerns
Most of the time, malocclusion is treated for cosmetic reasons. Children, however, may not want treatment because they will have to wear braces. It is usually possible to schedule the beginning of treatment for a time that is convenient for the child and the parent. Talking with children or teenagers and obtaining their input about treatment may be beneficial in increasing compliance. Full compliance with the orthodontist's instructions helps to ensure that the treatment is successful.
Resources
BOOKS
Bishara, Samir E., ed. Textbook of Orthodontics. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2001.
Subtelny, Daniel J. Early Orthodontic Treatment. Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Company, 2000.
PERIODICALS
"Duration of Pacifier Use, Thumb Sucking May Affect Dental Arches." Journal of the American Dental Association 133, no. 2 (December 2002): 1610–12.
Kluemper, G. Thomas, et al. "Early Orthodontic Treatment: What are the Imperatives?" Journal of the American Dental Association 131, no. 5 (May 2000): 613–21.
ORGANIZATIONS
American Association of Orthodontists. 401 North Lindberg Boulevard, St. Louis, MO 63141-7816. (800) STRAIGHT Fax: (3314)-997-1745. Web site: http:///www.braces.org.
American Dental Association. 211 East Chicago Avenue, Chicago IL, 60611-2678. (312) 440-2500. Web site: http://www.ada.org .
Tish Davidson, A.M. Bethany Thivierge
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: